Post Views: 8,318
ViewsNursing Care for Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease, which is a progressive and irreversible neurodegenerative condition, is found to be the most common form of dementia in the elderly population. In simple terms, dementia can be defined as a brain disorder that could affect the person’s ability to perform everyday activities. Typically, it would start after the age of 60 and the risks would increase as the person grows older and older. The risks of contracting Alzheimer’s disease are also found to be higher if the family member has the disease.
Nursing Goals for Alzheimer’s disease:
It’s to be understood that nurses play a major role in the identification of Alzheimer’s disease among the hospitalized elders. This has to be done by examining the patients for the signs of the disease right at the admission process itself. As such, there is no actual cure for Alzheimer’s disease and hence, the interventions for the disease should be aimed at promoting the patient’s functionality, as well as independence.
In addition to these primary goals, the nursing care goal for Alzheimer’s disease would aim at promoting the safety of the patient and independence in their self-care activities. Yes, of course, as a nurse, your goal should also include the reduction of a patient’s anxiety and agitation, enhancing their communicating abilities, providing room for socialization and intimacy, taking care of their nutrition, and supporting or educating their family members and caregivers about the disease.
Diagnostic Examination of Alzheimer’s disease:
Usually, Alzheimer’s disease will be diagnosed clinically from the patient’s history, family history, and clinical observations. As such, the presence of neurological or neuropsychological features will also need to be looked upon during the diagnosis. In general, the following medical imaging techniques will be used to exclude the other types of dementia:
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
- Positron emission tomography (PET)
Moreover, these techniques can also predict the transition of the patient from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease.
So, this is all about the overall diagnostic examination. The following section will speak about the nursing diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease in particular:
A Nurse’s Role:
The role of nurses with Alzheimer’s disease would involve finding out if there is a self-care deficit in the patient that is in relation to the cognitive impairment, as well as motor functioning. These include daily activities like:
- Bathing
- Hygiene
- Eating
- Toileting
- Cognitive ability
- Social interaction skills
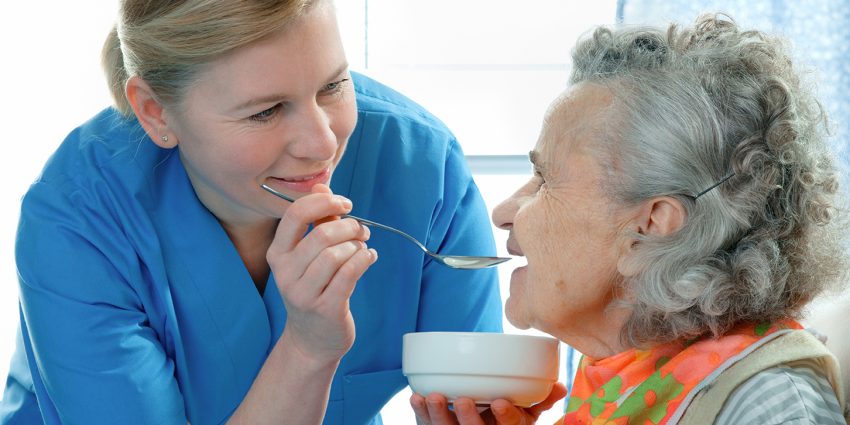
As such, the nursing care for Alzheimer’s disease patients in these activities would include self-care assistance in the following areas:
- Oral health management
- Behavior management
- Body image enhancement
- Emotional support
- Goal setting
- Exercise
- Discharge planning
In addition to this, another role for nurses with Alzheimer’s disease patients would include finding out if there is a risk for injury in relation to disorientation, confusion, weakness, and so on.
What to Expect in Patient Care:
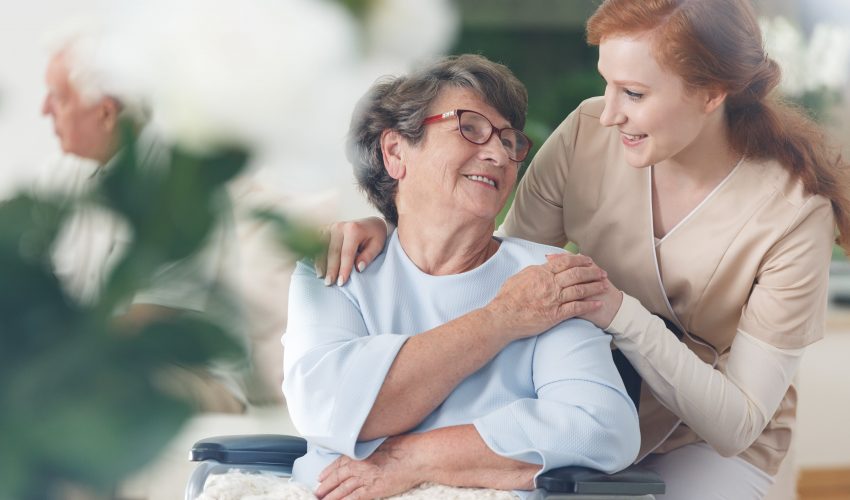
Nursing is a complex and diverse field and today’s nurses hold several functions to carry out in their duty. One such area is caring for Alzheimer’s disease patients, and caring for a patient with Alzheimer’s disease is not an easy task. This puts up the necessity of having competent persons in the field. Every stage of the disease would need support from the specialists. While it’s true that it’s important for the people to coordinate with each other in the therapeutic team, the role of nurses in dealing with Alzheimer’s disease patients is quite special.
The role of a nurse in Alzheimer’s disease would aim at decreasing the load on the caregiver when, at the same time, maintaining the independence of patients in their daily life for as long as possible. His or her role not only includes the caring for the Alzheimer’s disease patients when the caregiver cannot, it also involves supporting them. As a nurse, a person is expected to accompany, support, and help identify the sources of help. Also, she is expected to educate, as well as facilitate the patient’s access to specialist care whenever needed. She also has a role to play in the patient’s social assistance.
As a nurse, you should strive to offer the highest quality of life to the affected person, as well as the caregiver, when striving to prevent the complications of the disease. Furthermore, the educational role of the nurses is highly significant here, particularly, when it comes to the care of Alzheimer’s disease, so that the caregiver needs to be prepared for offering such care to the affected patients. Overall, the nursing interventions should be able to enhance the quality of life of the patients, as well as the caregiver.
One comment on “Nursing Care for Alzheimer’s Disease”
Leave a Reply
Nursing Care for Alzheimer’s Disease
By nurseadvisorofficial
Nursing is a complex and diverse field and today’s nurses hold several functions to carry out in their duty. One such area is caring for Alzheimer’s disease patients, and caring for a patient with Alzheimer’s disease is not an easy task.













This Blog Is Very Helpful And Informative For This Particular Topic. I Appreciate Your Effort That Has Been Taken To Write This Blog For Us. Radial head fracture treatment, Nursing diagnosis for head injury, nursing management of head injury, head injury blood clot treatment, nursing management of head injury patient, medical management of head injury, surgical management of head injury, care of patient with head injury, forehead bump treatment, head injury surgery. physiotherapy in Hyderabad